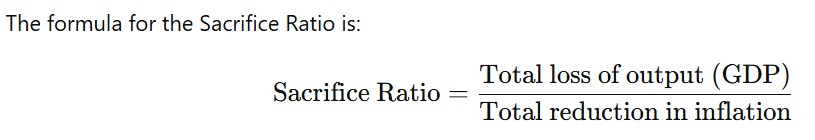The Sacrifice Ratio is closely related to A.W. Phillips’ Phillips Curve in the late 1950s. Sacrifice Ratio gained fame during the 1970 period of Stagflation.
The Sacrifice Ratio measures the cost (in terms of lost GDP or production loss) that a country must endure in order to achieve a reduction in inflation.
Percentage of output lost for each point reduction in the inflation rate is called Sacrifice Ratio.
Here, the Total loss of output refers to the amount of GDP that is lost as the economy reduces inflation, and the Total reduction in inflation is the decrease in inflation rate (usually measured in percentage points).
In other words, it represents how much economic activity (usually GDP) or employment must be sacrificed to achieve a certain reduction in inflation.
✅ Example:
If inflation drops by 2%, and during that time, the economy’s GDP falls by 6%, the sacrifice ratio is: 6 / 2 = 3%
Meaning 3% of GDP was lost for every 1% fall in inflation.