Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs 🧠
Abraham Maslow, a prominent psychologist, developed the Hierarchy of Needs theory in 1943. According to Maslow, human beings have a set of needs that are organized in a hierarchical structure. These needs must be satisfied in a specific order, beginning with the most basic and progressing toward higher-level needs. Maslow’s theory is often depicted as a pyramid, with five levels that represent different categories of needs.
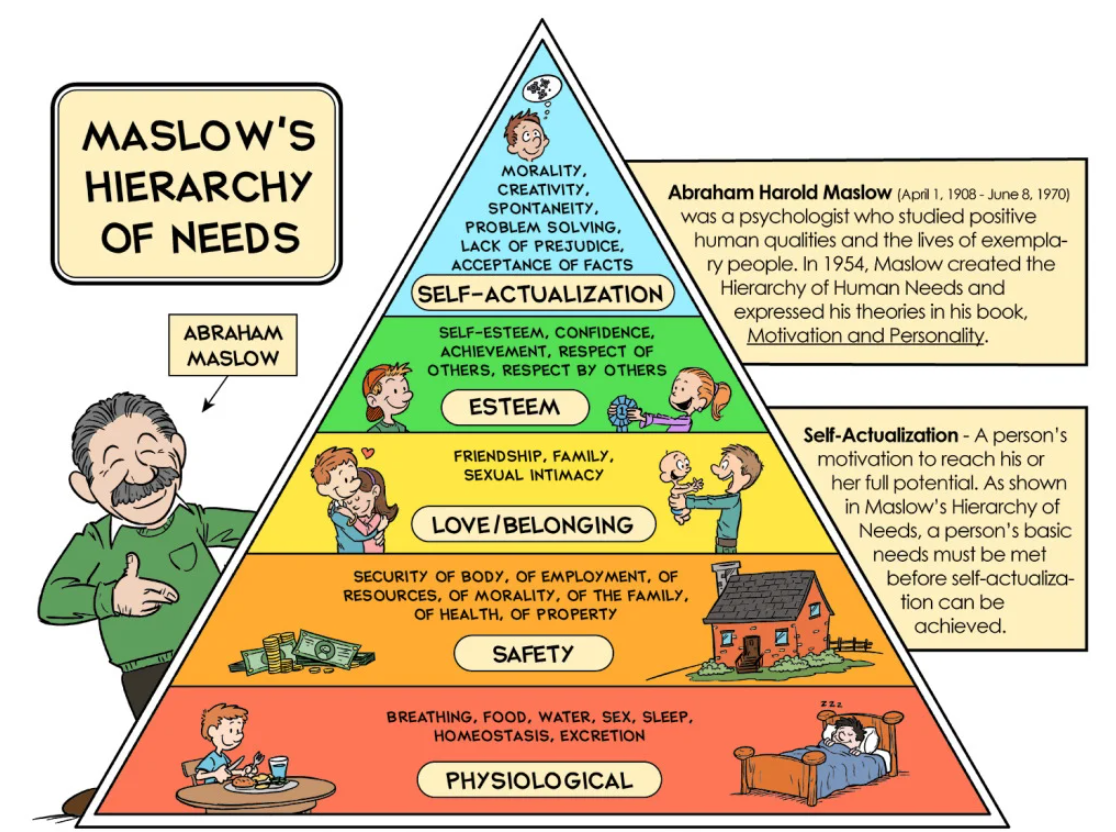
1. Physiological Needs 🍞
At the base of Maslow’s pyramid are physiological needs, which are the fundamental requirements for human survival. These needs include the necessities for life such as food, water, air, shelter, sleep, and warmth. Without fulfilling these basic needs, a person’s ability to focus on other areas of life is severely limited. These are the most basic and primary needs, and they must be met first before any other needs become motivating forces.
-
Examples: 🍽️ Food, 💧 Water, 🌬️ Air, 🏠 Shelter, 🛏️ Sleep, 🩺 Medical care.
2. Safety Needs 🛡️
Once physiological needs are met, the individual’s focus shifts to safety needs. These needs encompass both physical safety and emotional security. People seek to feel safe from harm, danger, or threats, both in their immediate surroundings and in the larger society. This category includes needs for stability, protection, and freedom from fear. It also extends to financial security and a stable living environment.
-
Examples: 🛑 Physical security, 💼 Employment, 🏥 Health insurance, 💵 Financial stability, 🏡 Safe living conditions.
3. Love and Belonging Needs ❤️
After safety is ensured, individuals begin to seek out love and belonging. This third level of needs involves the human desire for social connections and relationships. Humans are social creatures, and the need to form emotional bonds with others is essential to psychological well-being. This includes the desire for friendships, family relationships, and romantic connections. A lack of social interaction or feelings of isolation can lead to distress and dissatisfaction.
-
Examples: 🤝 Friendships, 💕 Romantic relationships, 👨👩👧👦 Family ties, 👫 Social groups, 🌍 A sense of community.
4. Esteem Needs 🏆
Once love and belonging needs are satisfied, people strive to meet esteem needs. These needs are concerned with the individual’s sense of worth, respect, and accomplishment. There are two components to esteem needs: self-esteem, which involves the individual’s own sense of personal achievement and confidence, and esteem from others, which includes recognition, status, and respect from others. Fulfilling esteem needs fosters feelings of competence, accomplishment, and dignity.
-
Examples: 💪 Self-respect, 🏅 Confidence, 🏆 Achievement, 👏 Recognition, 🌟 Respect from others.
5. Self-Actualization 🌟
At the top of Maslow’s pyramid is self-actualization, which represents the fulfilment of an individual’s potential. This level involves the desire to become the best version of oneself, achieving personal growth and pursuing meaningful goals. Self-actualization is about realizing one’s abilities, talents, and creativity, and striving to become the most authentic, complete version of oneself. Maslow believed that self-actualization is unique to each individual and may look different for everyone.
-
Examples: 🎨 Personal growth, 🎭 Creativity, 🧩 Problem-solving, 🏅 Achieving one’s life goals, 🌱 Realizing one’s full potential.
Progression Through the Hierarchy 🚀
Maslow suggested that individuals are motivated to fulfil their needs starting from the bottom of the pyramid. Lower-level needs must be satisfied before individuals can focus on higher-level needs. For example, a person who is struggling to meet their basic physiological needs (e.g., food, shelter) will not prioritize social relationships or esteem. Similarly, an individual who lacks safety and security will not be concerned with self-actualization until their basic safety needs are met.
It is important to note that not everyone reaches the self-actualization stage. According to Maslow, only a small number of individuals fully achieve this level, as it requires a continual process of personal growth and self-reflection.
Criticisms and Revisions 🔄
While Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs has been influential in understanding human motivation, it has faced criticism. Some researchers argue that the hierarchy is too rigid, suggesting that people may pursue higher-level needs even when their lower-level needs are not fully satisfied. For example, individuals may seek social relationships or pursue creative endeavours despite lacking basic safety or physiological needs.
In later years, Maslow himself revised his model to include additional needs such as cognitive needs (knowledge and understanding) and aesthetic needs (appreciation for beauty), highlighting that human motivation is more complex than initially proposed.
Conclusion 🎓
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs offers a comprehensive framework for understanding human motivation. It underscores the idea that individuals are motivated by a series of hierarchical needs, starting with the most basic and progressing toward higher-level goals. By fulfilling these needs in order, individuals strive to achieve personal satisfaction, emotional well-being, and self-actualization.