🎯 Directional Corporate-Level Strategy:
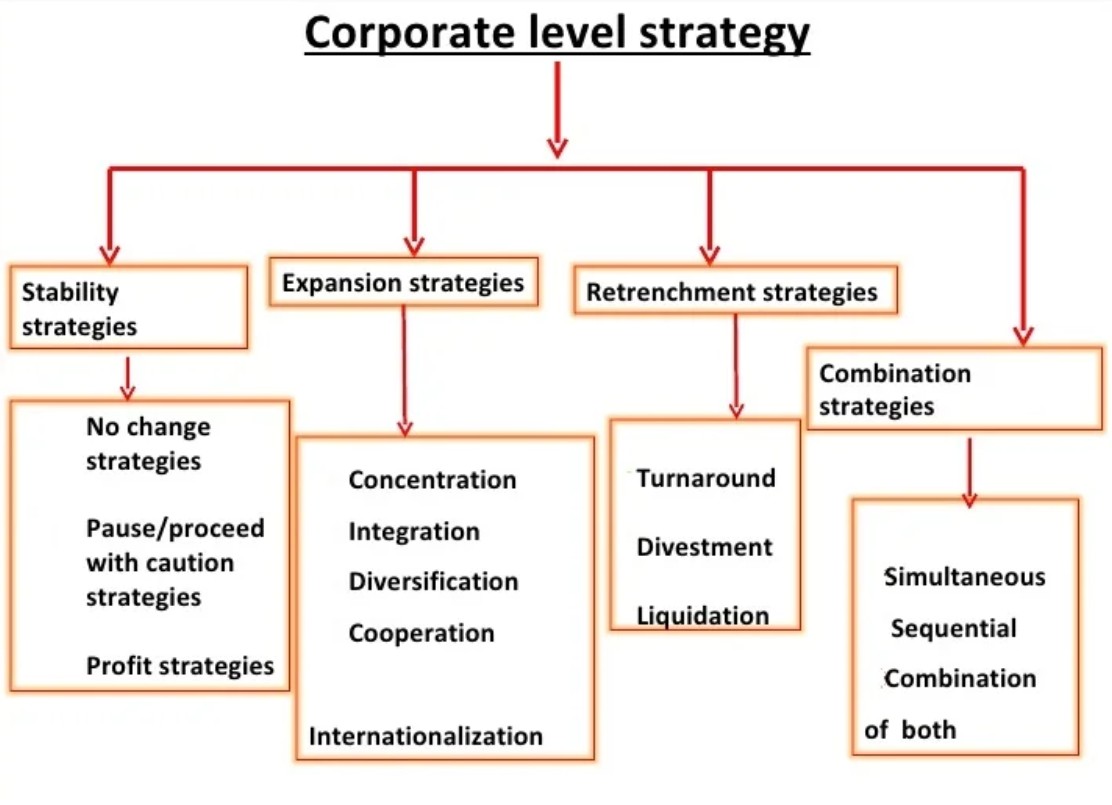
1. Concentration Strategies
-
Definition: Focus on a single business or industry to strengthen the company’s position in that particular market.
-
Goal: Grow by increasing market share, improving products, or expanding the customer base within the current industry.
-
How:
-
Market penetration (selling more to existing customers).
-
Market development (entering new geographic areas).
-
Product development (introducing new or improved products).
-
-
Example: A smartphone company focusing only on enhancing its smartphone models instead of diversifying.
2. Retrenchment Strategies
-
Definition: Reduce the company’s scope or size to improve financial stability or focus on core areas.
-
Goal: Cut costs, improve efficiency, and stabilize the company during tough times.
-
Example: Nokia selling its mobile phone division to focus on network infrastructure.
- The reasons for pursuing a retrenchment strategy typically include:
- Better opportunities in the environment are perceived elsewhere – Companies may focus on core competencies and exit underperforming areas.
- The environment is seen so threatening that internal strengths are insufficient to meet the challenge – When external threats are significant, retrenchment allows firms to protect resources and avoid further losses.
- The firm is not doing well or perceives itself as doing poorly – Retrenchment helps to address weaknesses and stabilize the company.
-
Types:
-
Turnaround (revive a struggling business)
-
Divestiture (sell off parts of the business).
-
Liquidation (close and sell assets of the business).
-
Downsizing (reduce workforce or operations).
-
3. Simultaneous and Sequential Strategies
-
Simultaneous Strategies:
-
The company pursues multiple strategies at the same time across different business units or markets.
-
Example: A conglomerate growing some businesses (growth strategy) while downsizing others (retrenchment strategy) simultaneously.
-
-
Sequential Strategies:
-
The company pursues strategies one after another in a planned sequence.
-
Example: A company might first stabilize its current operations (stability strategy), then invest in growth afterward.
-
4. Stability Strategies
-
Definition: Maintain the current business operations without significant change.
-
Goal: Consolidate and strengthen existing operations, avoid risk, and preserve current market position.
-
When used:
-
In mature industries with little growth.
-
When external conditions are uncertain or unfavorable.
-
When the company is performing well and wants to avoid unnecessary risks.
-
-
Example: A utility company continuing to operate its existing services without expanding or contracting.