📘 Porter’s Generic Competitive Strategies
Michael Porter, a renowned professor at Harvard Business School, introduced the General Competitive Strategies in his 1985 book Competitive Advantage.
These strategies help businesses gain a competitive edge in the marketplace and focus on how a company can create and sustain competitive advantage.
📊 Key Dimensions of Strategy
Porter’s Generic Strategies are based on two key dimensions:
-
🎯 Scope of the Market:
-
🌍 Broad (industry-wide)
-
🎯 Narrow (focused/niche)
-
-
🧩 Source of Competitive Advantage:
-
💰 Cost (lower cost)
-
🌟 Differentiation (unique offering)
-
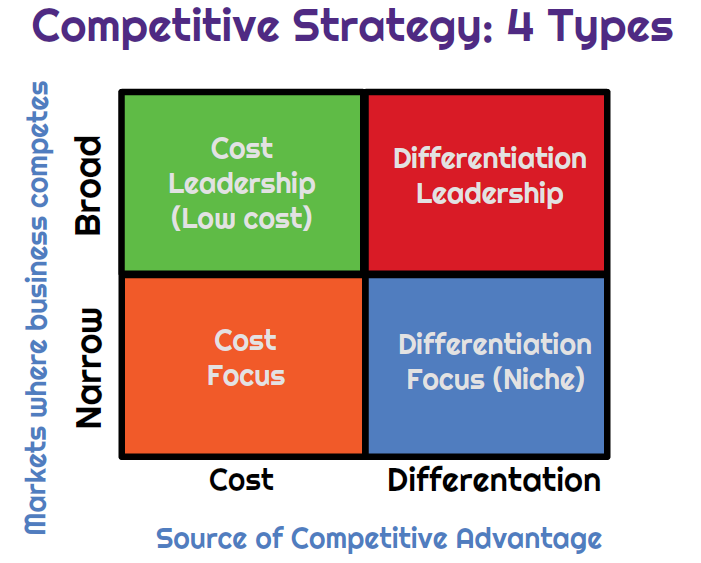
🔷 The Four Generic Strategies
By combining these dimensions, we get four strategic segments:
🔹 1. Cost Leadership
(Broad Scope + Cost Advantage)
-
🎯 Goal: Become the lowest-cost producer in a broad market.
-
⚙️ How: Streamlined operations, economies of scale, tight cost control.
-
📈 Outcome: Ability to underprice competitors or maintain average prices with higher margins.
-
🛒 Example: Walmart — offers low prices to a wide customer base.
🔹 2. Differentiation Leadership
(Broad Scope + Differentiation Advantage)
-
🎯 Goal: Offer unique products/services across a broad market.
-
💡 How: Superior quality, innovation, brand image, or customer service.
-
💵 Outcome: Charge premium prices due to perceived added value.
-
🍏 Example: Apple — broad appeal with uniquely designed, high-quality tech products.
🔹 3. Focused Cost Leaders
(Narrow Scope + Cost Advantage)
-
🎯 Goal: Be the lowest-cost provider in a niche market.
-
⚙️ How: Specialized cost efficiencies tailored to a specific segment.
-
📉 Outcome: Serve a small group better or cheaper than broader competitors.
-
🇮🇳 Example: DMart — low-cost retail targeting price-sensitive Indian consumers.
🔹 4. Focused differentiators
(Narrow Scope + Differentiation Advantage)
-
🎯 Goal: Offer highly specialized, differentiated products to a niche market.
-
🧠 How: Deep understanding of unique customer needs in a narrow segment.
-
🔒 Outcome: Strong brand loyalty and premium pricing in that niche.
-
⌚ Example: Rolex — luxury watches targeting high-end consumers.
📋 Summary Table:
| 🧭 Strategy | 🌐 Competitive Scope | 🧩 Competitive Advantage | 🌟 Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 💰 Cost Leadership | Broad | Cost | Walmart |
| 🌟 Differentiation | Broad | Differentiation | Apple |
| 💸 Cost Focus | Narrow | Cost | DMart (India) |
| 💎 Differentiation Focus | Narrow | Differentiation | Rolex |