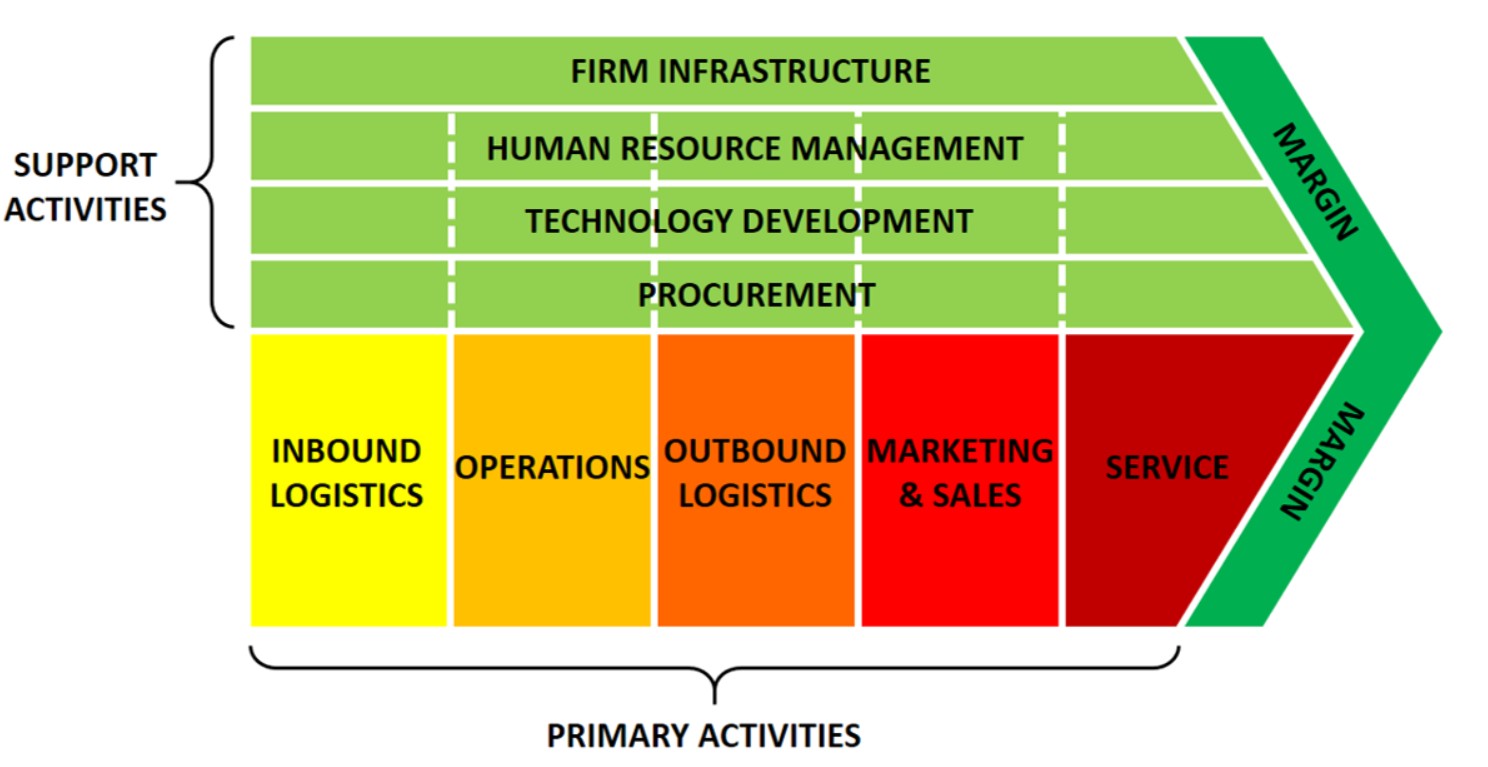
📘 What is Value Chain Analysis?
- Value Chain is a string of activities that moves a product from the raw material stage through manufacturing and distribution, and ultimately to the end user.
Value Chain Analysis (VCA) is a strategic management tool introduced by Michael Porter in his 1985 book Competitive Advantage.
It’s used to analyze the internal activities of a business and identify where value is created (or destroyed) in the process.
By examining these activities, companies can optimize their operations, improve efficiency, and achieve a competitive advantage.
🧩 What is a Value Chain?
A Value Chain refers to the series of activities that a company performs to deliver a valuable product or service to the market. It includes everything from raw materials to the final customer experience.
The goal of value chain analysis is to understand how each of these activities adds value to the final product or service.
🔑 Primary Activities in the Value Chain:
These are activities that are directly involved in the creation of a product or service.
-
Inbound Logistics
-
Handling, storing, and distributing raw materials or components.
-
Example: Managing the supply of raw materials or components (e.g., parts for a smartphone).
-
-
Operations
-
Converting inputs into the final product through manufacturing or assembly.
-
Example: The production process at a car manufacturer.
-
-
Outbound Logistics
-
Distributing the final product to customers or retailers.
-
Example: Shipping finished products to retailers or customers.
-
-
Marketing & Sales
-
Promoting and selling the product or service.
-
Example: Advertising campaigns, promotions, sales teams, or e-commerce platforms.
-
-
Service
-
Post-sale services that enhance the product’s value.
-
Example: Customer support, maintenance services, product repairs, or upgrades.
-
🔑 Support Activities in the Value Chain:
These activities support the primary activities and contribute indirectly to the company’s performance.
-
Firm Infrastructure
-
General management, planning, finance, legal, and quality control.
-
Example: The administrative backbone of the company that supports all other activities.
-
-
Human Resource Management
-
Recruiting, training, and development of employees.
-
Example: Hiring skilled workers, training them, and offering performance incentives.
-
-
Technology Development
-
Research and development (R&D), product design, and technological improvements.
-
Example: Investment in new technologies to improve production processes or enhance product features.
-
-
Procurement
-
Acquiring resources, materials, and services from suppliers.
-
Example: Purchasing raw materials, components, or services that the company needs to create products.
-
📊 Value Chain Analysis: Competitive Advantage
The ultimate goal of Value Chain Analysis is to find out where the company can create a sustainable competitive advantage. Companies can gain an edge by:
-
Reducing costs at certain points (e.g., efficiency in operations).
-
Differentiating the product (e.g., innovation in technology development).
-
Delivering higher value (e.g., excellent customer service).
📋 Summary of the Value Chain:
| Primary Activities | Examples |
|---|---|
| Inbound Logistics | Sourcing raw materials |
| Operations | Manufacturing the product |
| Outbound Logistics | Distributing to customers |
| Marketing & Sales | Advertising, promotions |
| Service | Post-sale support, repairs |
| Support Activities | Examples |
|---|---|
| Firm Infrastructure | Management, finance, planning |
| HR Management | Hiring, training employees |
| Technology Development | R&D, product design, software |
| Procurement | Acquiring resources and supplies |